But first — a quick look at the seller’s dilemma with generative AI
To GPT or not to GPT?
That is the question on many sellers’ minds as generative AI dominates the conversation (pun intended) and makes its way into every LinkedIn post, Forbes article, SaaS product, and sales process.
While the swift onset of LLMs (large language models) left an already shaken corporate community scrambling to catch up after a year of massive change, no one is more affected than sellers, who have become the primary targets (alongside marketing) of AI products designed to be virtual assistants and promising at minimum a 10% productivity boost.
Sellers also have the customer experience to consider, which raises questions about quality, best practices, the human/technology balance, and authenticity in interpersonal interactions, among others.
Questions like:
- Which tasks should I use AI for?
- Which tasks are best left to a human?
- How will using AI impact my relationship with my customers?
- How will AI impact my role?
- Can I trust the information I get from AI?
- There are already so many AI tools — which ones are most useful to me?
Are you a revenue leader grappling with these questions? Get in touch to quickly get caught up to speed on the practical applications of AI in go-to-market organizations.
Generative AI adoption rate by sellers: A survey
As both users and vendors of AI products and proponents of a better buying experience, we have a vested interest in the ethical and effective application of these tools throughout the sales cycle.
To that effect, we surveyed a cross-section of professionals in typical B2B roles, including: sellers with different levels of seniority, sales enablement professionals, marketers, product managers and developers, and customer success managers.
An interesting trend emerged from our survey.
65% of those surveyed across all roles responded “yes” when asked if they use generative AI to perform their jobs. A deeper dive into the data showed the percentage of those specifically in sales related roles experimenting with AI during their daily workflow was also 65%.
The percentage of sellers using AI was also the lowest adoption rate compared to 70% of product and engineering roles, 71% of marketers, designers, and creative roles, 67% of customer success roles, and 100% of HR roles.
The survey shows that while the majority of B2B professionals are jumping into AI in some form regardless of role, sellers are the most reluctant of any group to do so.
So how can sellers intelligently use generative AI tools to get all the gains while sidestepping any of the risks holding them back?
Take a look at the pros, cons, “shoulds,” and “shouldn’ts” of using generative AI for sales, taken from the survey responses of sellers who are already using it.
The pros: How sellers can take advantage of generative AI
Generative AI is already helping copywriters draft content and computer programmers write code, boosting their productivity by 50% or more. It can do the same for salespeople.
— Harvard Business Review: How Generative AI Will Change Sales
Here’s how sellers are already using generative AI in their day-to-day workflow.
- Filling in gaps in my skill set, such as email writing.
- Saving time on reading or research through Q&A with the AI and/or summarization of lengthy documents.
- Use as a microlearning tool to get quick refreshers on information before calls.
- It’s useful for developing pitches, understanding business personas, competitor product info, sales objections, etc.
- Prepping for meetings by learning important terms/jargon/concepts that are important to a person in a specific industry or even at a specific company.
- Asking specific questions about how content and/or products can help a [role/persona] be more efficient at [their goal/problem to solve].
- Automating time consuming tasks that allow me more time to prospect and sell.
- Creating fake content to fill demo environments.
- The best instances of AI are when it can help answer not only the "what" but the "what now" of a prompt or insight.
- AI has been helpful in the way it summarizes information and can write an email on the content.
- Editing research on a topic, customer, etc.
- Use cases where the heavy lifting is taken away: Type up an email suggestion, summarize a meeting/chat discussion/next steps, summarize the key areas of a training course, suggest questions to ask to help me prepare for a meeting, suggest key news events that I should know about when preparing for a customer meeting that could be used as general conversation.
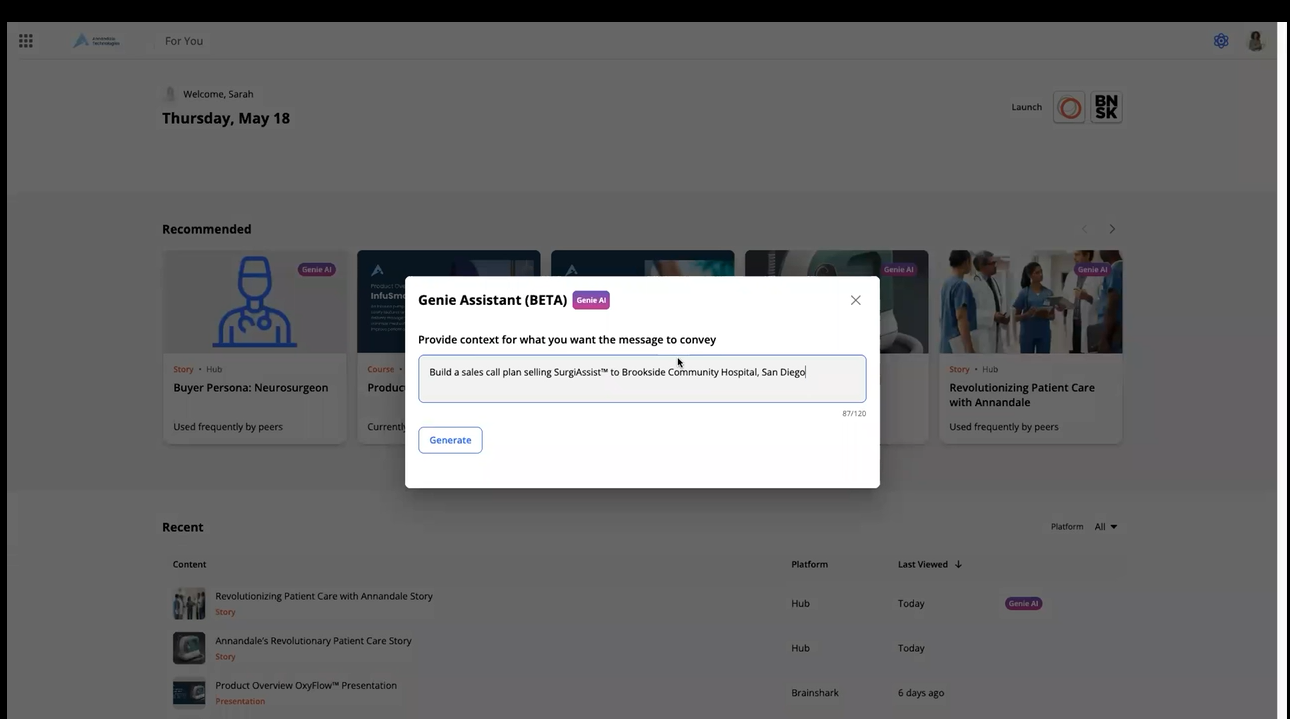
Bigtincan's GenieAI sales assistant in Beta. Get a demo.
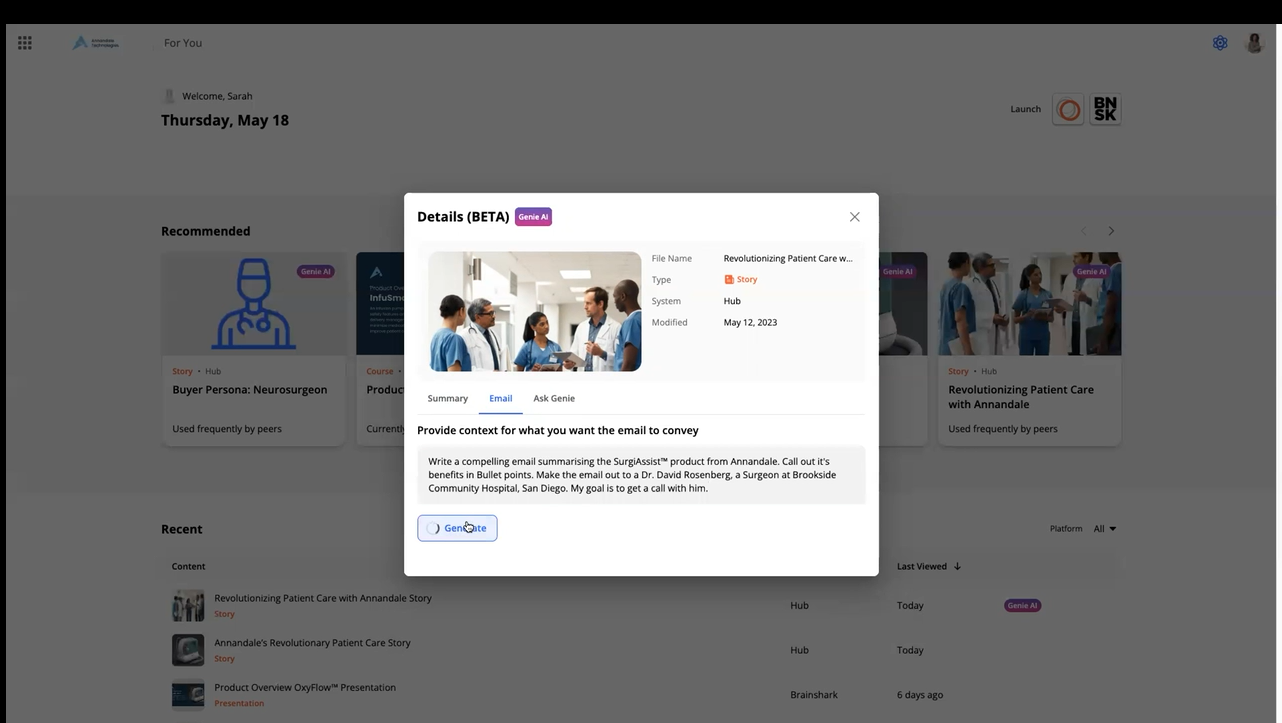
The cons: How NOT to use generative AI in sales
From IP infringement to data privacy and security, there are a number of issues that require thoughtful mitigation strategies and governance. The need for human oversight and accountability is clear, and may require the creation of new roles and capabilities to fully capitalize on opportunities ahead.
- McKinsey: AI-powered marketing and sales reach new heights with generative AI
These are instances where sellers said they use caution with generative AI or avoid it entirely.
- Don't let it replace human interaction and being yourself — make your interactions with customers authentic.
- Be wary of bias/manipulation in the information provided.
- Don’t automate responses back to prospects who are part of in-flight deals. All of that should be personalized except maybe content curation.
- Be sure to verify all information that is AI generated to make sure it is accurate and on point for your use case. Never just copy and paste an AI generated response.
- Don’t give open/public AI tools any proprietary information or comparisons around ideas, data, or strategies that shouldn't be made publicly available, due to the lack of privacy controls.
- I'd be careful when using AI to generate emails b/c prospects can easily tell if it's generated with a simple browser plugin. If you do use email generators, be sure to personalize it.
- I'm still leery of relying on AI to give me new information that I'm not familiar with (how would I know if it was hallucinating or not?).
- Anything that needs the most current factual info or linked sources doesn't work. I asked GPT for a LinkedIn post with links to a supporting article and the links didn't work.
- Decision making or creation without review. It can be biased, erroneous, or misleading so the review action is a necessary step.
- Over reliance on it for holistic data since the response is only as valuable as the prompt and the context provided.
- To not take everything it says to be true or take exact words when reusing it. Also do not use it as the source of truth for things such as medical questions.
- Don't rely on it for personalization tasks — nobody would like to feel you are being lazy by using AI. I would encourage it to do menial tasks so sellers can focus on high value tasks.
Key takeaways
Overall, sellers praised AI’s ability to help a human be more efficient, but not replace or impede their way of tackling their work.
Top 3 areas where sellers find value in generative AI tools:
- Customer research.
- Meeting prep/microlearning.
- Help with email writing.
Top 3 areas where sellers avoid AI or use caution:
- Entering in or generating content about proprietary/sensitive information.
- Hitting “send” without proofing information or editing emails.
- Using it for any task or customer interaction that should be human, authentic, and personalized.
Whether you’re new to using generative AI in your sales role or looking to expand your usage, consider these general “rules of thumb” that will grant you a productivity boost without affecting your customers’ experience.
Explore more ways to use AI for sales (and get more original research) in: How AI-powered sales coaching improves your pitch.
